Internet Key Terms Explained Part 3
posted in Information guides by Kelly on 14:44 Jun 1st, 2016
· Over the last few weeks I have been publishing blog posts with a brief explanation of what some of the terms and words used in relation to the internet and computers mean. This is such a mammoth task that it has been broken down into an ongoing series of posts. The list is in no order and covers some basic things and others more advanced. Here is the next part of the blog series. The weather here appears to have taken a turn for the worst this week so it may give you something to keep you busy in the absence of mowing the lawn! So in no particular order here are some more terms for you...
T
- Address Bar This is usually found at the top of your browser (see previous blogs). You can type in internet website addresses or search terms into this bar to look up information using whatever search engine (see below) you have your browser set to use. You will notice this as it says http://www. In it followed by the URL (see below) of the website you are visiting in our case this would end sivillservice.co.uk It will change depending on the website you are on. When you are looking something up on Google (for example) it is important to check the address that you go to in order to ensure the website is genuine.
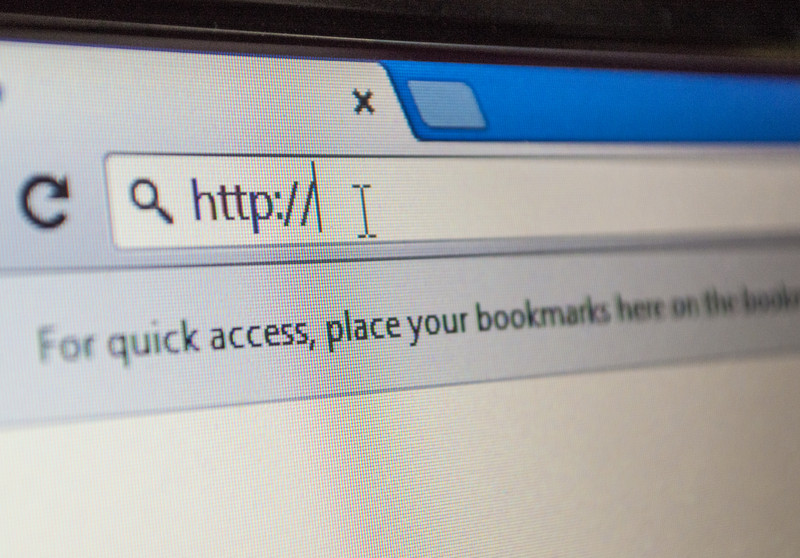
- URL This stands for Uniform Resource Locator. It is commonly called a web address. It acts as a pointer to find the resources that are held in a specific location. This location is called a domain. The domain will be hosted on a specific server that holds all the resources that relate to that particular website. When you visit a website you are requesting for your computer via the internet to locate that specific location and this information is then displayed to you in easy, bitesize chunks as a website or webpage. Where the request is very specific e.g. if you were to visit a particular product page on Amazon then the URL can be very long and complex.
- Website This is a collection of webpages that contain content from the same person. Let me give you an example..our website located at sivillservice.co.uk contains a selection of different pages that we have created. They all start with sivillservice.co.uk/ then have a variety of different locations that point to the different resources and information that are on each individual webpage. Some contain photos and slides others are simply written text but they all come together to form our website. When you visit a website usually the page that you land on is referred to as a landing page or homepage. It is usually the introductory page that tells you about the person, company, band or products that the person who owns the site has to offer. If you search for a particular product then what you get taken to will be a product page instead of a homepage but there will be a link you can click that will take you to that particular websites homepage. In 2014 the internet hit 1 billion individual websites. There is something for everyone. All website domains have to be registered through a company that then ensures that they are listed with the W3C – the people who rule over the internet as an active and owned site that is there for people to go visit. A company will then host that site and its resources. In our case a company called Store Express (part of the Advansys group) host our site and email for a nominal fee every month.
- Search Engine This term seems these days to have become somewhat synonomous with Google BUT Google is not the only search engine but is by far the biggest. When people design and build websites they do so in the hope that Google will like it and display it at the top of the relevant list when people search for terms that the website relates to. Millions of pounds and dollars are spent every year optimising websites for search engines. A search engine is a means of searching all the websites on the internet (or the ones the that search engine knows about) for particular images, information or media. When you carry out a search it will then return results that are displayed in a list manner. At the top of the list you will have a few ads from companies that have paid to be there when the thing you looked for is searched. Under that is what are called organic results. These are dynamic and will change all the time depending on how much that search engine likes that site. Search engines search for information based on algorithms (see below) and they rank (display) websites based on another algorithm. Sometimes search engines will update this algorithm and this will change the way in which websites are displayed. Google carries out over 100 billion searches per month so it just goes to show how many people use them. Others include yahoo! Bing and Ask.
- Algorithm Put in simple terms and algorithm is a set of instructions laid out step-by-step based around some very complex maths. These can include data processing, numeric calculations and reasoning tasks. Nearly every computer based task revolves around the use of algorithms. They are also responsible for security encryption. It is a simple sounding term and explanation for something that in reality is very complex and a very specialised area that underpins pretty much everything to do with computers and thus supermarket checkouts, ATM machines, airport air traffic control, the internet and everything else computer related.
- USB Universal Serial Bus. This is a connector and socket type found on all computers and laptops. Most tablets, phones and even printers have USB sockets these days. On phones and tablets it is a slight variation in being a microusb rather than full size USB but some do have full sockets. My tablet has both and I have an adaptor that I can plug in to give extra sockets too.
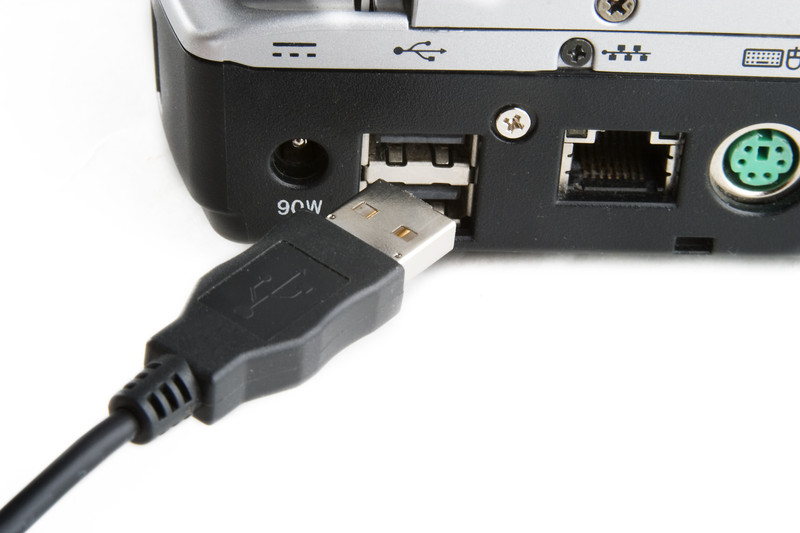

USB sockets are found everywhere these days. We have one on our car stereo to play music, the TV to playback videos, photos and music. I can be certain that you will have seen these somewhere. USB sockets started as a USB 1.0 and quickly developed into 2.0 version. This is still in common use today. Now we have USB 3.0. This is much faster than the previous versions and also more reliable.
More will follow on part 4 over the next week but if you have any suggestions please feel free to contact me. Feedback is always welcome!
Thanks
Kells x